Frontiers Multiple Ehrlichia chaffeensis genes critical for persistent infection in a vertebrate host are identified as nonessential for its growth in the tick vector; Amblyomma americanum
€ 25.50 · 4.8 (733) · In Magazzino

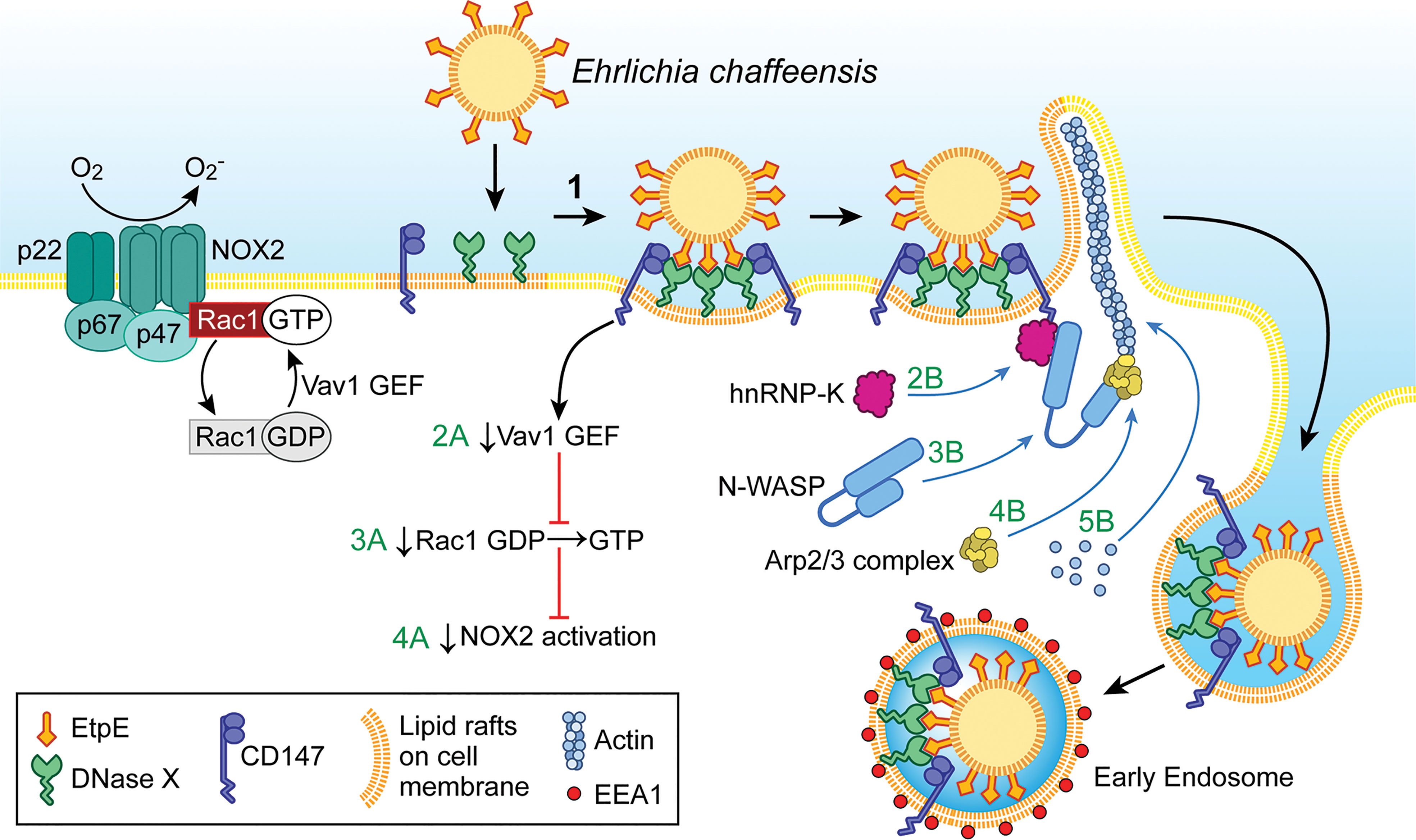
Frontiers The “Biological Weapons” of Ehrlichia chaffeensis: Novel Molecules and Mechanisms to Subjugate Host Cells

Monocytic ehrlichiosis - List of Frontiers' open access articles

Natural History of Ehrlichia chaffeensis: Vertebrate hosts and tick vectors from the United States and evidence for endemic transmission in other countries - ScienceDirect
ENY-2067/IN1327: Ehrlichia and Anaplasma
Rickettsia, Ehrlichia, Coxiella and Bartonella

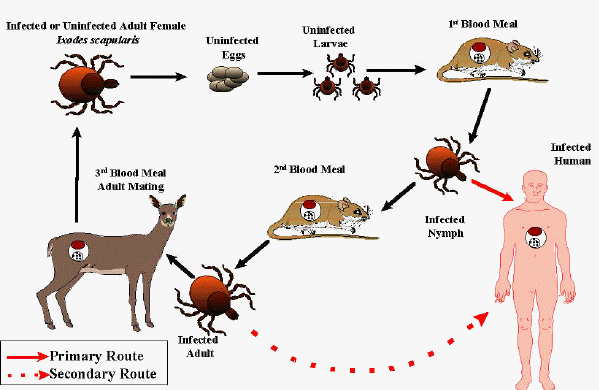
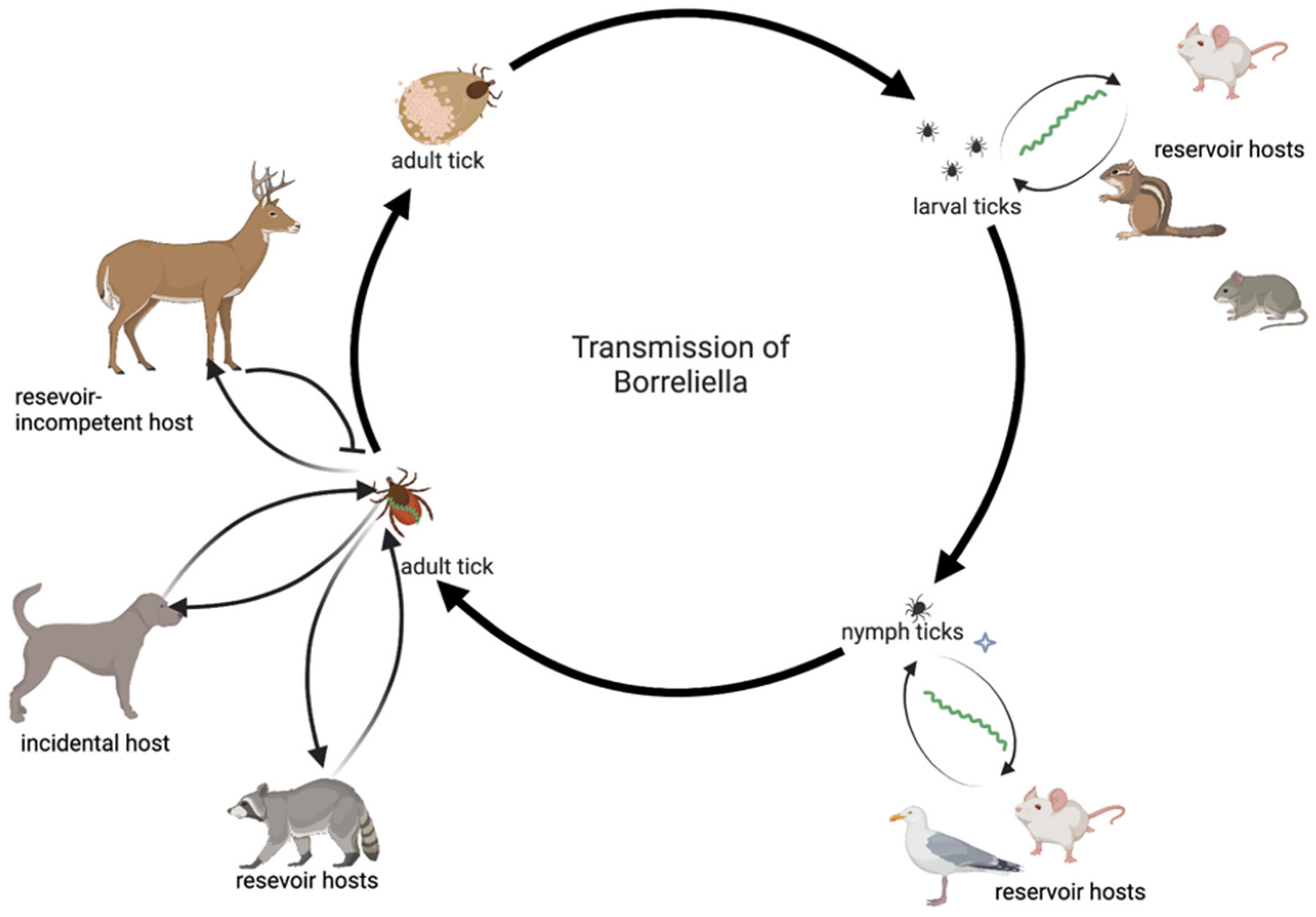
Tick-borne pathogen transmission. This image shows the life cycle of
Ehrlichia chaffeensis Infection in the Reservoir Host (White-Tailed Deer) and in an Incidental Host (Dog) Is Impacted by Its Prior Growth in Macrophage and Tick Cell Environments

Ecological and evolutionary perspectives on tick-borne pathogen co- infections - ScienceDirect
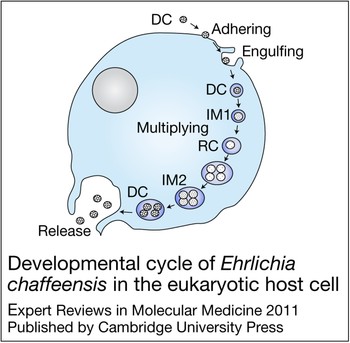
Molecular and cellular pathobiology of Ehrlichia infection: targets for new therapeutics and immunomodulation strategies, Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine
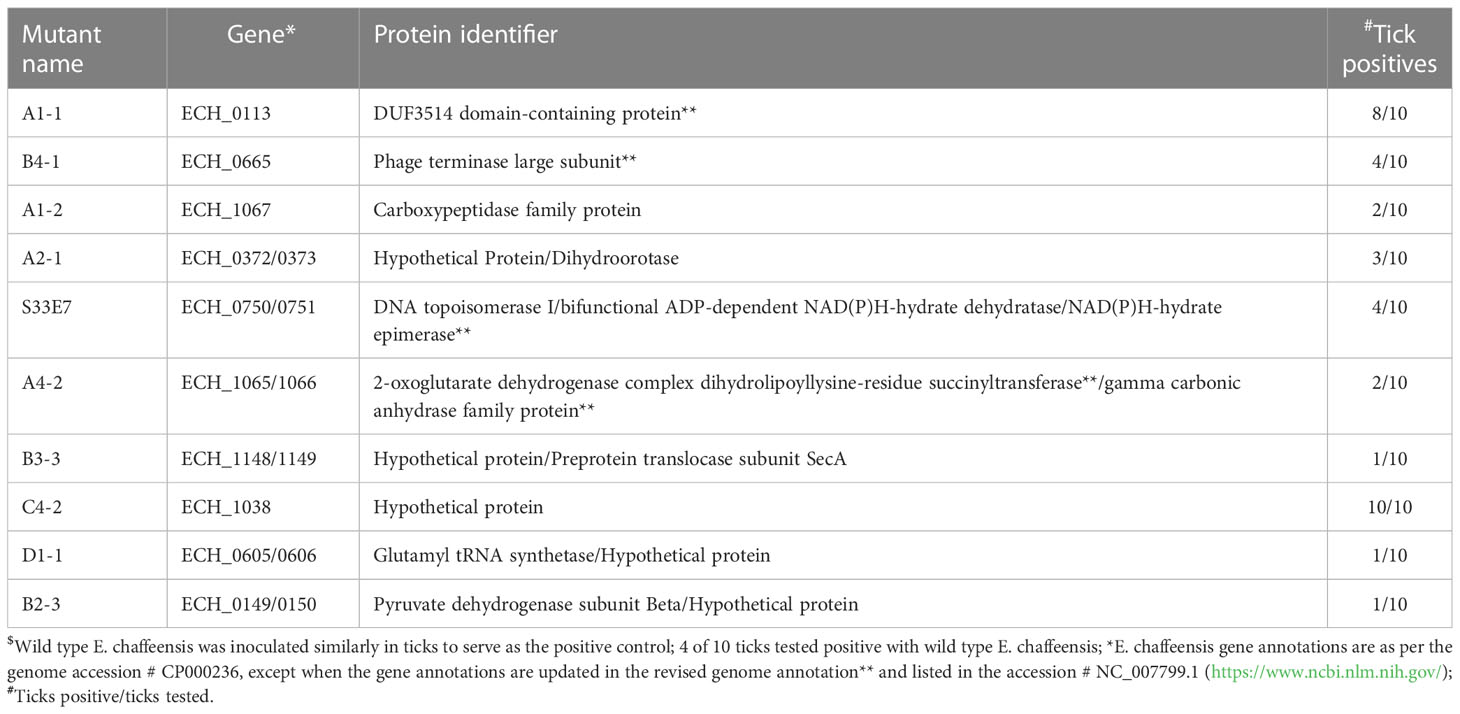
Frontiers Multiple Ehrlichia chaffeensis genes critical for persistent infection in a vertebrate host are identified as nonessential for its growth in the tick vector; Amblyomma americanum

Multiple Ehrlichia chaffeensis Genes Critical for Its Persistent Infection in a Vertebrate Host Are Identified by Random Mutagenesis Coupled with In Vivo Infection Assessment

An Entry-Triggering Protein of Ehrlichia Is a New Vaccine Candidate against Tick-Borne Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis

Frontiers Advances in the Study of the Tick Cattle Microbiota and the Influence on Vectorial Capacity
Genes, Free Full-Text

Ehrlichia species, their host, diseases, and vectors.chaffeensis is